Hispanic culture is justly renowned on a global scale, as its historical diversity has given the world an astonishing artistic output in architecture, literature, culinary arts, painting, and, of course, music.
In this article, we will focus on the latter, which is perhaps the best known in the public consciousness, if only for its popular culture. Our focus, however, will be more on the general Mexican musical tradition, with a special emphasis on regional music musical instruments, and music history, somewhat in the same way that NineCasino platforms have all types of games, but to a greater extent slot games.
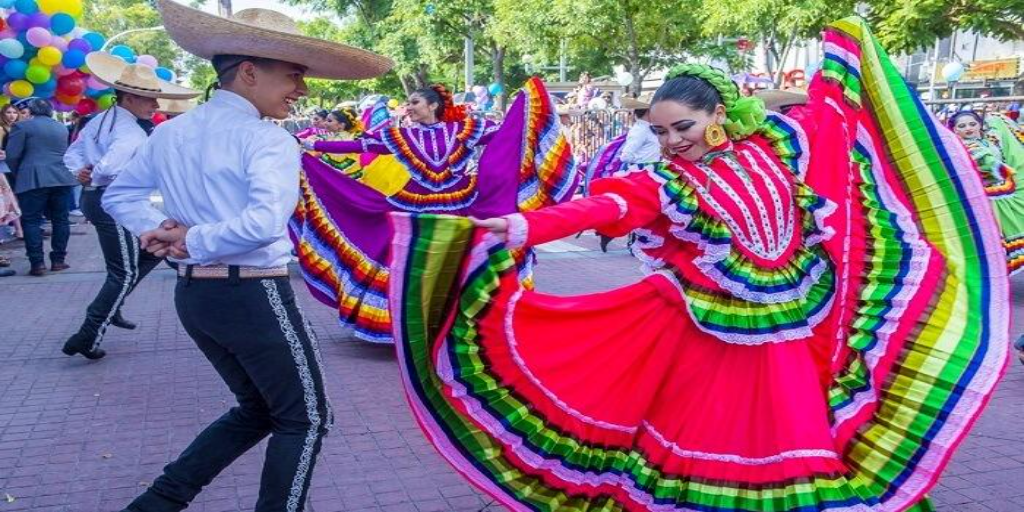
For Hispanic people, music is one of the central elements of life, and this is reflected in their attitude, as it is extraverted, colorful, upbeat, and surprisingly energetic, despite the deep spiritual and political issues it expresses in some cases. So whatever Hispanic celebration or festival you attend, you are sure to encounter salsa, merengue, and flamenco. All of these have strong rhythmic elements through musical instruments such as guitars, drums, and various horns.
What is the Basis of Mexican Music?
Narrowing our focus, it can be said that the music of the Mexican people is so diverse because it combines different genres and performance styles, due to the influence of many cultures. Among these, the influence of European, African, and, of course, indigenous Mexican influences can be highlighted as the most prominent. This is presumably one of the reasons why the creators of the 5Gringos casino chose a Hispanic design for the interface, while the NineCasino site is more streamlined but no less unenjoyable.
Mexico gained its independence in the early 19th century, after 300 years of Spanish rule. Almost immediately after independence, the mestizaje was launched, which called for the strengthening of common cultural traits, with the support of the government, to create a common national identity, and had a significant impact on all artistic sectors. Thus, music became the main expression of Mexican nationalism during this century, hence mariachi was created. Through his unrelenting efforts since then, UNESCO inscribed this type of Mexican music on the Representative List of the Intangible and Cultural Heritage of Humanity in 2011.
Drawing on indigenous sounds and heritage, Mexican music has also inspired modern contemporary artists such as Elvis Presley. More than one of his works, inspired by Hispanic culture, can also be heard in several films.
The Main Instruments of Mexican Music
The indigenous Mexicans used drums, flutes, rattles, trumpets, and singing to make music, and they invented dances to accompany the resulting music. This is where the roots of contemporary Mexican music can be found, but the real foundations were laid during the Spanish occupation.
Over time, different instruments have become more traditional in different regions, just as it depends on a gambler’s game style whether they prefer 5Gringos or NineCasino, but some commonalities remain, both in music and game styles. The following is a list of the main musical instruments used in the folk music of the different regions, broken down by region:
- Northern Mexico: accordion, bajo sexto, snare drum, tuba. Folk music from these areas is called Corrido and Banda.
- Central Mexico: bajo sexto, guitar, violin, trumpet. Mariachi and Tamborazo Zacatecano originate from this area.
- Southern Mexico: harp, classical and requinto guitars, jarana jarocha, marímbula. We can thank the locals for the creation of folk music such as Son Jarocho and Chilena.
The Historical Development of Mexican Music
Given that the United States of Mexico is a fairly large country, it is not surprising that there was no unified musical tradition and that customs varied from region to region. It was only during the mestizaje, in the 19th century, that national music started to appear. Its theme was often patriotic, hence military bands soon began to emerge.
The president at this time invited Jaime Nuno, who composed the music for the Mexican national anthem. Over the next few years, he composed more important works and was joined by several other classical music artists, resulting in the founding of the National Conservatory of Music in 1866.
By the end of the 19th century, the Portifiratio was launched, with the support of the liberal president of the time. In the process, the basic Mexican musical styles, the Mexican national music, were expanded. They were influenced by cosmopolitan and European regional music, such as polka and mazurka. It was also the beginning of an interest in opera among the Mexican elite.
Each region also had its national anthem, most notably the Oaxacan waltz Dios nunca muere, which wonderfully combined deep Catholic religiousness with patriotic love. This was a period of artistic flowering in Mexico, as not only music but also dance, poetry, and literature, became increasingly colorful and developed.











![Sarkodie – You & I [Remix] ft. Olivetheboy Sarkodie – You & I [Remix] ft. Olivetheboy](https://trendyhiphop.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/Sarkodie-You-I-Remix-artwork-150x150.jpg)



















Leave a Reply